Conservative and Surgical Treatment Options for Herniated Discs
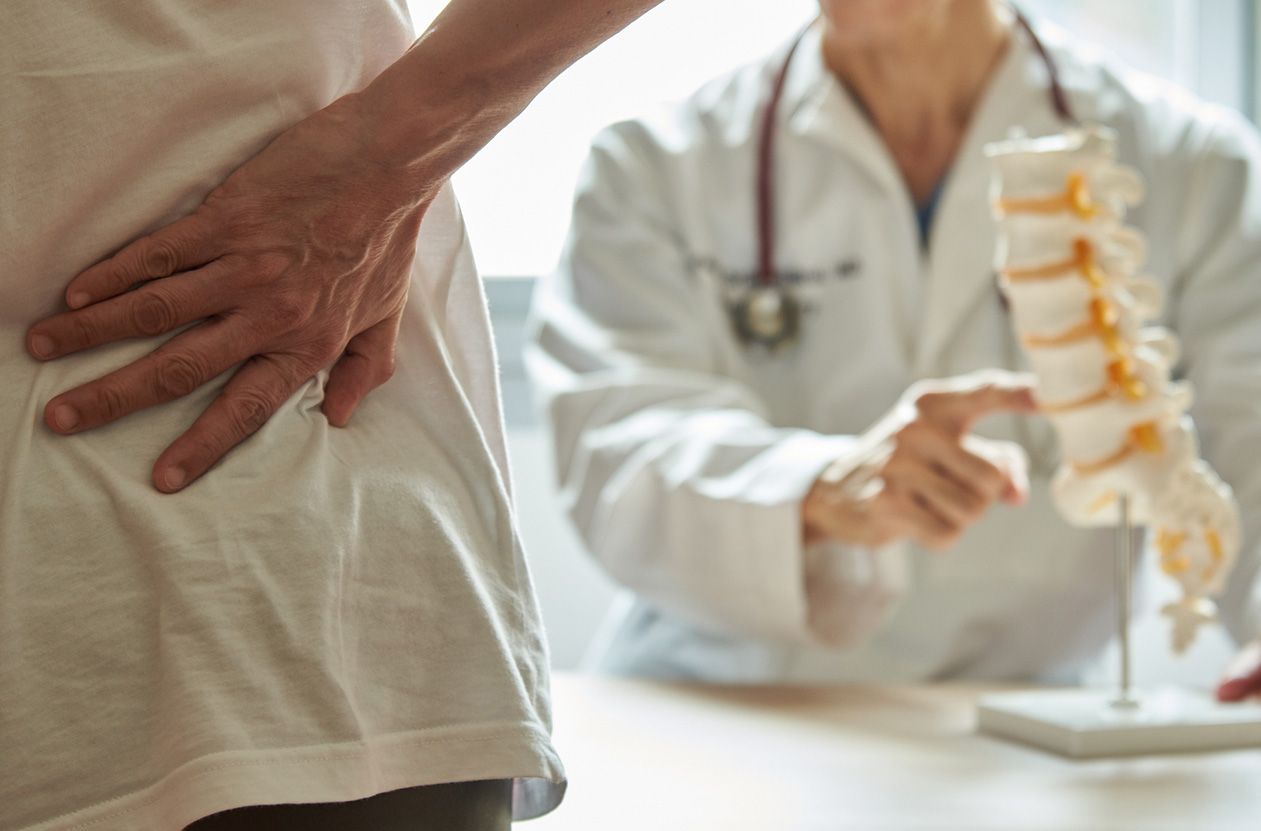
Think of your spinal discs as small, rubbery cushions that separate the bones in the spine from one another. Sometimes, these discs rupture or bulge. This is what physicians mean when they talk about herniated discs, which can cause one or more of them to press against spinal nerves. And yes, it can be just as painful as it sounds.
Most happen in the lumbar spine. They don’t just cause pain, but sometimes also weakness, numbness or tingling in other parts of the body. Not all herniated discs need special attention. They often cause no pain at all. But they can also cause chronic pain and other problems, and these patients need medical attention to get their lives back on track.
What Is a Herniated Disc?
A disc “herniates” or ruptures when the soft center of the disc pushes through the outer wall and toward the spinal canal. For many people, this is caused over time by typical wear and tear. For others, heavy lifting or a sudden motion can cause small cracks or tears that form in the disc’s outer wall.
If you’re experiencing pain from one, you might have a nerve that is being pinched or irritated by the affected disc. Discs are supposed to act as shock absorbers for the vertebrae. They allow the spine to twist and bend. A herniated disc and the ensuing pain can limit a person’s ability to move and perform even simple daily tasks.
Conservative Treatments
Pain can make a person impatient, but treating back pain – with or without surgery – is a process that takes time.
Most people with pain from a herniated disc start with some combination of rest and methods of reducing inflammation and managing the pain. A good doctor might also suggest improvements to your posture or daily habits. In most cases, patients try out different treatments to see what works best them.
Physical Therapy (PT)
Physical therapy is one of the best ways to rebuild strength and mobility in any part of the body. Physical therapists will work on a patient over a span of weeks or months to educate them and help them with small exercises. They usually design a home exercise program aimed at restoring function, mobility, and strength – both in the back and in the surrounding areas. PT is often used in conjunction with other non-invasive treatments.
Medication
Anti-inflammatory medications and muscle relaxers are also common treatments for a bulging or ruptured disc. Your doctor might prescribe them initially to control pain or reduce swelling in the affected area. Medication can offer temporary relief but it won’t cure the underlying issue. Ideally, your treatment plan should help you manage the pain enough to handle daily tasks, sleep at night, and avoid surgery.
Epidural Steroid Injections
If oral medications aren’t working, another option is to have steroid-based drugs injected into the problem area near the spine. By aiming the injection at the space between the spinal bone and nerves, this is a more targeted way to reduce inflammation-causing pain. Steroid injections are often used in tandem with physical therapy.
Surgical Treatments
Only a small percentage of people with a herniated disc end up getting surgery. However, if you’ve attempted medication and PT treatments and your injury is still limiting your ability to function, then it might be time to look at surgical options more closely.
Orthopaedic physicians at our clinics only perform surgery after conservative methods have proven to be ineffective. They recommend the most minimally invasive option that best addresses your needs. You might be a candidate for surgery if you’re in reasonably good health and:
- Your pain is impairing your quality of life,
- You have difficulty standing or walking, or
- Progressive neurological deficits develop
If so, recommendations could include one of these common surgical treatments:
Discectomy
The most common surgery for a lumbar herniated disc, a discectomy involves the removal of the disc that has become herniated. This relieves pressure on nerves the herniated disc is pressing on. A discectomy might also include removing part of or all of the back portion of spinal bones in front of the herniated disc so that the surgeon is able to access the disc.
Fusion
If your problem stems from a lack of stability around the affected area, you might undergo a spinal fusion, which involves fusing two or more spinal bones together. Doctors will sometimes recommend fusion if the cushioning discs between the vertebrae have worn away. The purpose is to provide strength and added stability in the affected area.
Artificial Disc
Sometimes, if a disc is herniated, physicians can replace it with an artificial one. This procedure is relatively new and is sometimes used as an alternative to fusion.
Keep in mind that any of the above surgeries would only be considered if a physician can first pinpoint the exact source of the problem.
If you’re suffering from pain related to a possible herniated disc, the Minimally Invasive Spine Clinic at MidAmerica Orthopaedics is a great place to get your questions answered. You can schedule a preliminary visit with one of our expert physicians, who will take it from there. Give us a call at 708-237-7200 or schedule an appointment online.

